What does ARP mean? ARP is actually an address resolution protocol, namely ARP (Address ResoluTIon Protocol), which is a TCP/IP protocol for obtaining physical addresses based on IP addresses.
1. What is the ARP protocol?
ARP protocol, the full name of "Address Resolution Protocol", the Chinese name is the address resolution protocol, using the ARP protocol can obtain the physical address (MAC address) of the corresponding host through the IP address.
The ARP protocol belongs to a protocol in the TCP/IP protocol that resolves an IP address into a MAC address, and is located at the network layer in the TCP/IP five-layer model. This protocol is used to resolve the physical address corresponding to the IP address in the local area network.
To put it simply, when host A sends an IP datagram to another host B over the network, it will first send it to the router on the network where host A is located, and then the router will determine whether the destination address is in the network, and if so, it will be forwarded directly to The destination host in this network; otherwise, it will continue to pass to the next route until it reaches the router of the specified network, and the router of the specified network will send this datagram to the destination host.
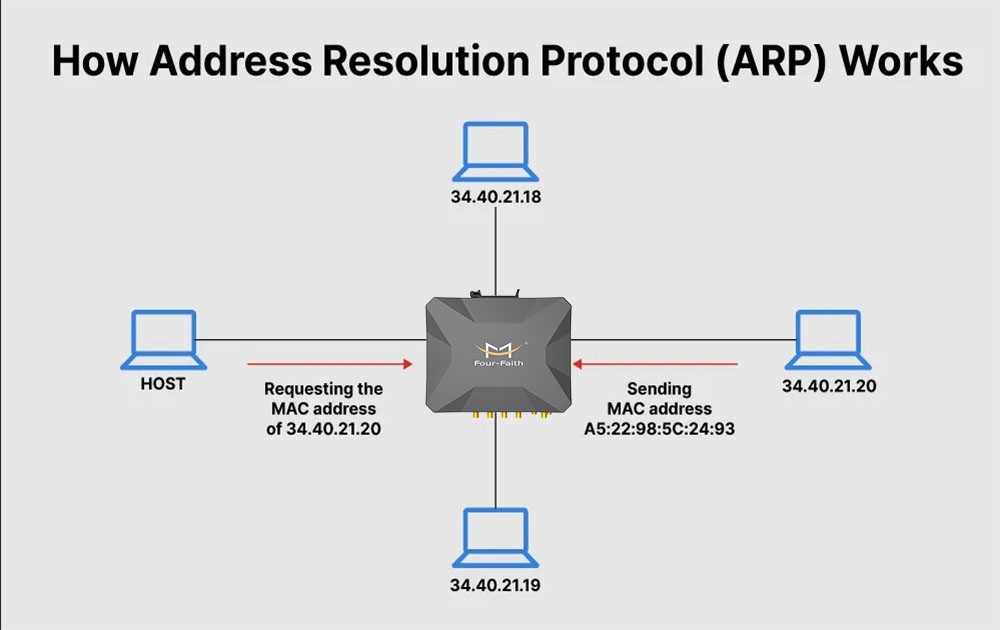
The whole process will eventually involve the process of sending data to a host in the network by a router (or gateway) of a network. In this process, the router usually sends an ARP broadcast request, requesting that the host whose IP address is consistent with the destination IP address of the data packet return its own MAC address to the router, because the data transmission of the data link layer is transmitted through the physical address.
The ARP request will be broadcast to all hosts in the LAN. After other hosts in the network receive the ARP request, check the IP address of the host that sent the ARP request, store the IP address and its corresponding MAC address in the ARP cache, and check this Whether the IP address requested in the ARP request is its own IP address, it sends an ARP reply, and the reply contains its own IP address and the corresponding MAC address. After the router in the network obtains the MAC address, it can correctly transmit the data packet to the destination host through the data link layer.
The so-called "address resolution" is the process by which the host converts the target IP address to the target MAC address before sending the frame. The basic function of the ARP protocol is to query the MA address of the target device through the IP address of the target device, so as to ensure the smooth communication between hosts.
The ARP protocol is somewhat similar to DNS. The difference is: DNS is the resolution between domain name and IP. In addition, ARP protocol does not need to configure services, while DNS needs to configure services.
The ARP protocol requires that both communicating hosts must be in the same physical network segment (ie, a local area network environment)!
ARP overview:
1.1 The full name of ARP is "Address Resolution Protocol"
1.2 Obtain the MAC address of the host through the IP address in the LAN.
1.3 The MAC address is the physical address of the 48-bit host, which is unique within the local area network.
1.4 The ARP protocol is similar to the DNS service, but does not need to configure the service.
1.5 The ARP protocol is a three-layer protocol.
2. What is the ARP protocol used?
ARP can solve the mapping problem of IP addresses and MAC addresses of hosts or routers in the same LAN.
When the host sends information, it broadcasts the ARP request containing the target IP address to all hosts on the network, and receives the return message to determine the physical address of the target; after receiving the return message, the IP address and physical address are stored in the local ARP The cache is kept for a certain period of time, and the ARP cache is directly queried for the next request to save resources.
ARP commands can be used to query the correspondence between IP addresses and MAC addresses in the local ARP cache, and to add or delete static correspondences. Related protocols are RARP and proxy ARP. NDP is used to replace the Address Resolution Protocol in IPv6.
3. What is the arp spoofing: ARP spoofing (security risks)
The arp protocol (Address Resolution Protocol) is based on the mutual trust of each host in the network. The hosts on the network can send ARP reply messages independently. When other hosts receive the reply message, they will not detect the authenticity of the message. It will be logged into the local ARP cache.
In this way, an attacker can send a fake ARP reply message to a certain host, so that the information sent cannot reach the expected host or reach the wrong host, which constitutes an ARP spoofing.
ARP spoofing can cause the communication between the target computer and the gateway to fail, and even lead to communication redirection. All data will pass through the attacker's machine, so there is a great security risk.
Defensive measures
Don't base the network security trust relationship on IP or MAC (RARP also has the problem of deception). The ideal relationship should be based on IP+MAC.
Set a static MAC--"IP correspondence table, do not let the host refresh the set conversion table.
Unless absolutely necessary, stop using ARP and keep ARP as a permanent entry in the corresponding table.
Use an ARP server. The server looks up its own ARP translation table to respond to other machines' ARP broadcasts. Make sure this ARP server is not hacked.
Use "proxy" to proxy IP transmission.
Use hardware to shield the host. Set up routes to ensure that IP addresses can reach legitimate paths (statically configured routing ARP entries). Note that using switching hubs and bridges will not prevent ARP spoofing.
The administrator periodically obtains a RARP request with the IP packet of the response, and then checks the authenticity of the ARP response.
The administrator polls periodically to check the ARP cache on the host.
Use a firewall to continuously monitor the network. Note that when SNMP is used, ARP spoofing may cause trap packets to be lost.
If you are infected with ARP virus, you can clear the ARP cache, specify the ARP correspondence, add routing information, and use anti-virus software.