The netmask generally refers to the subnet mask. Subnet mask (subnet mask), also known as network mask, address mask, subnet mask, is used to indicate which bits of an IP address identify the subnet where the host is located, and which bits identify the host's bitmask.
1. What is netmask - Netmask Range
Netmasks (or subnet masks) are a shorthand for referring to ranges of consecutive IP addresses in the Internet Protocol. They used for defining networking rules in e.g. routers and firewalls.
Every entity (server or client) communicating on the internet will have a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address. Most commonly, these addresses are written human-readable notation as follows: 192.168.0.1. This describes and IP version 4 addess. (The internet is moving towards the IP version 6 standard to allow for more resources to be addressed).
An IP address is actually just a unique binary number - IPv4 allows for around 4.3 billion addresses and one time, IPv6 expands the address space to 3.4×1038 addresses.
In networking, it is convenient to talk about groups of addresses to help with networking. For instance, different internet providers will be awarded ‘chunks’ of consecutive addresses, so internet routers need only read the start of each IP address before deciding to pass TCP packets off to known network node.
1.1 A netmask is a shorthand for describing a range of IP addresses. A netmask may describe just a single IP address:
192.168.0.1/32: just the address 192.168.0.1
1.2 Or all possible IP addresses:
192.168.0.1/0: all 4.3 billion addresses from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
1.3 More usefully, it does something in between:
192.168.0.1/31: the IP addresses 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.0.1
2. How to read a netmask
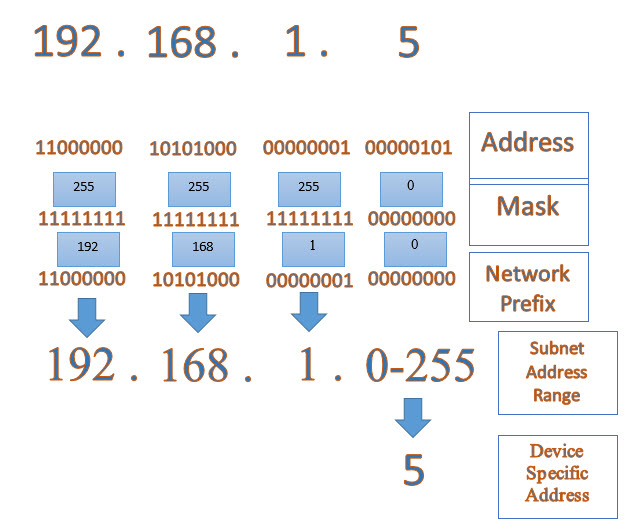
The left hand side of a netmask (e.g. 192.168.0.1) specifies a the host IP address. The right hand side specifies (e.g. /32) how many digits of the host address are significant, when considered as a binary number. Non-significant bits in the binary form are treated as a wild-card.
For instance, in the netmask 192.168.0.1/32, the host address is 192.168.0.1. This can be written in binary as 11000000.10101000.11111111.00000001. To match this netmask, an address must have match exactly 32 digits - i.e. have the same binary digit in each position. This means only one address will be matched by this pattern.
The netmask 192.168.0.1/31 states that the last binary digit is not significant, so will match two addresses: 11000000.10101000.11111111.00000000 and 11000000.10101000.11111111.00000001 (written more readably as 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.0.1).
Similarly 192.168.0.1/30 states that the last two binary digits are not significant, so will match four different addresses.
3. Netmask calculator
Ipcalc takes an IP address and netmask and calculates the resulting broadcast, network, Cisco wildcard mask, and host range. By giving a second netmask, you can design subnets and supernets. It is also intended to be a teaching tool and presents the subnetting results as easy-to-understand binary values.
Enter your netmask(s) in CIDR notation (/25) or dotted decimals (255.255.255.0). Inverse netmasks are recognized. If you omit the netmask ipcalc uses the default netmask for the class of your network.
Look at the space between the bits of the addresses: The bits before it are the network part of the address, the bits after it are the host part. You can see two simple facts: In a network address all host bits are zero, in a broadcast address they are all set.
The class of your network is determined by its first bits.
If your network is a private internet according to RFC 1918 this is remarked. When displaying subnets the new bits in the network part of the netmask are marked in a different color
The wildcard is the inverse netmask as used for access control lists in Cisco routers.
Do you want to split your network into subnets? Enter the address and netmask of your original network and play with the second netmask until the result matches your needs.